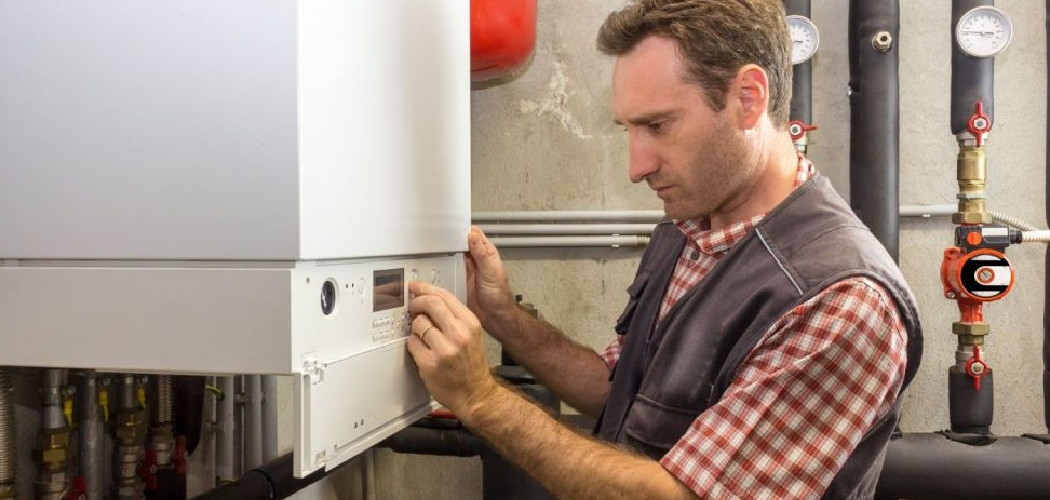
Draining a boiler is a vital process that homeowners may need to perform for various reasons, such as routine maintenance, conducting important repairs, or replacing specific components. While draining the boiler is an essential step, properly refilling it afterward is equally critical to ensure the system functions efficiently and reliably. Failure to refill the boiler correctly can lead to issues such as inconsistent heating, permanent damage to the unit, or even costly repairs down the line.

This article aims to provide a clear, step-by-step guide on how to refill boiler after draining, ensuring that you can complete the process safely and effectively. Additionally, it highlights common mistakes to avoid during the process to maintain optimal boiler performance and longevity. Understanding the importance of refilling your boiler carefully will not only help you save on unnecessary expenses but also ensure a warm, comfortable home environment throughout the year.
Why You Might Need to Drain and Refill a Boiler
Draining and refilling a boiler is an essential process that ensures the system runs smoothly and efficiently. This maintenance task may be required for various reasons, primarily to maintain and repair your heating system. Regular maintenance, such as flushing out sludge or sediment build-up, helps improve the overall efficiency and performance of your boiler.
Over time, deposits and debris can accumulate within the system, causing blockages or reducing heat output. Draining the boiler also becomes necessary when replacing components, addressing leaks, or dealing with frozen pipes during colder months.
Refilling the boiler after draining is equally critical to restore its functionality. A properly refilled boiler ensures the system operates at the optimal pressure, preventing overheating and promoting energy efficiency. It also mitigates potential issues like airlocks, which can disrupt water circulation, and helps prevent corrosion by maintaining the right balance of water and air within the system.
This process not only extends the lifespan of your boiler but also contributes to reliable heating, ensuring your home remains comfortable and warm throughout the year. Proper maintenance and timely refilling are key to avoiding costly repairs and maintaining consistent performance.
Materials and Tools Needed
Essential Tools
- Hose or Bucket: Used for draining the boiler, especially if it hasn’t been drained before refilling.
- Pressure Gauge: Necessary for accurately monitoring water levels and ensuring they remain within the recommended range.
- Bleed Valve Key: Required for releasing any trapped air in the radiator or boiler system during the process.
Materials Required
- Fresh Water: Essential for refilling the boiler to restore proper operation. Ideally sourced from a safe, clean supply, typically your home’s mains water line.
- Access to the Water Supply: Make sure to have ready access to your home’s water system to facilitate a smooth refilling process.
- Optional Water Treatment Chemicals: These can be added to maintain boiler efficiency by preventing scale build-up and corrosion, which can otherwise affect the system’s performance over time.
Having all these tools and materials prepared beforehand ensures the boiler refilling process is straightforward, efficient, and minimizes potential disruptions.
How to Refill Boiler After Draining: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Check the Boiler’s Water Pressure
Start by examining the boiler’s pressure gauge. This gauge indicates whether the water pressure is within the appropriate range. Ideally, most boilers function efficiently with a pressure between 1 and 1.5 bar. If the pressure is below this range, refilling the boiler with water is essential to restore optimal performance.

Step 2: Locate the Filling Loop
Next, identify the filling loop, which is usually situated near or beneath the boiler. The filling loop is either a flexible hose or a built-in valve used to introduce water into the boiler system. Ensure the filling loop is properly connected to both the water supply and the boiler before proceeding to the next step.
Step 3: Open the Filling Valve
Slowly open the filling valve to allow water to flow into the boiler system. You might hear the sound of water entering the system as this happens. Pay close attention to the pressure gauge as the pressure starts to increase. Be patient and avoid opening the valve too quickly to prevent overfilling the system.
Step 4: Close the Filling Valve
Once the pressure gauge indicates the correct level—usually between 1 and 1.5 bar—close the filling valve fully. Make sure the valve is securely turned off to prevent water from leaking. Double-check the gauge to confirm the pressure remains stable, and inspect the valve connections for any signs of drips or leaks.
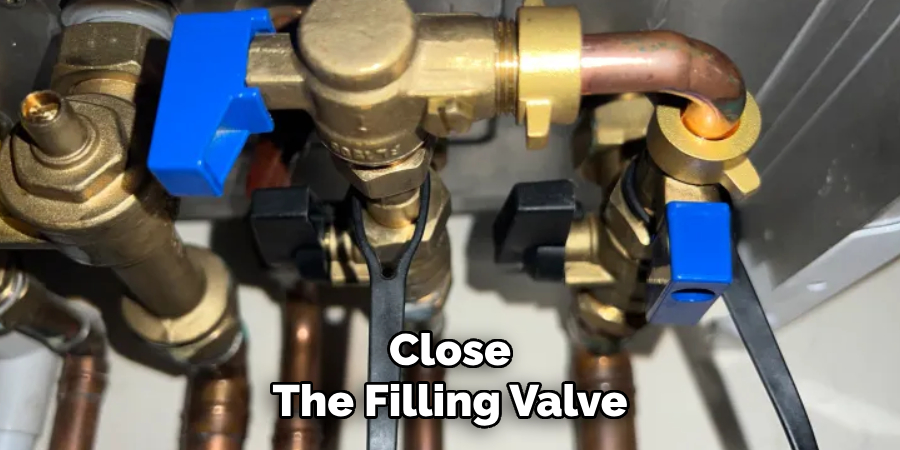
By following these steps carefully, you can ensure a safe and efficient boiler refilling process that supports optimal system functionality.
Bleeding the Radiators and Removing Airlocks
Why Bleeding is Necessary
Air can become trapped in the heating system during draining or refilling, which leads to inefficiencies such as cold spots on radiators or uneven heating throughout your home. This trapped air prevents hot water from circulating properly, reducing the effectiveness of your heating system and potentially causing higher energy bills.
How to Bleed Radiators
Bleeding radiators is a simple process that ensures optimal system performance. Start by turning off your heating system to avoid hot water spraying out during the process. Use a radiator key to gently open the bleed valve located at the top of each radiator. You’ll typically hear a hissing sound as the trapped air escapes. Once the hissing stops and water begins to flow steadily from the valve, close it tightly to prevent leaks. Keep a cloth or small container handy to catch any drips.
Repeat this process for each radiator in your home, starting with those located on the lowest floor and working your way upward. After completing the procedure, check the boiler pressure and top it up if necessary to maintain the correct level. Regularly bleeding radiators ensures a well-functioning and energy-efficient heating system.
Checking for Leaks and Ensuring Proper Functionality
Inspecting the System for Leaks
After refilling, take the time to carefully inspect the boiler and surrounding pipes for any visible leaks. Pay close attention to the connections and joints, as these are common areas where leaks may occur. Additionally, examine the valves, particularly the pressure relief valve, to ensure they are tightly closed and functioning correctly. If you notice any leaks, address them immediately by tightening the affected areas or seeking professional assistance, as unattended leaks can lead to significant damage and inefficiency in the heating system.
Running the Boiler
Once you are satisfied that there are no leaks, turn the boiler back on to restore the heating system. Allow it to run for a few minutes and monitor its functionality closely. Observe whether the radiators heat up evenly across your home and ensure that the boiler’s pressure remains stable at the desired level.
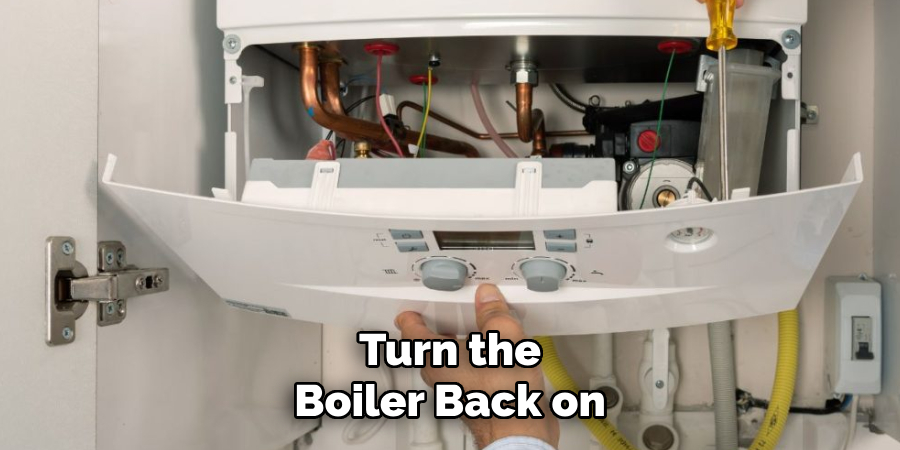
If the pressure fluctuates or the radiators fail to heat as expected, recheck the system for issues or consult a professional. Regular inspections help maintain a properly functioning and energy-efficient heating system, ensuring comfort and reliability throughout the colder months.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Low Pressure After Refilling
If the pressure continues to drop after refilling, it may indicate a leak within the system or an issue with the filling loop. Start by carefully inspecting all visible connections, including pipes, radiators, and valves, for signs of water leakage. Look for dripping, pooling water, or corrosion around joints. If no visible leaks are found but the pressure still drops consistently, there might be internal issues that require professional inspection. Addressing potential leaks promptly helps prevent further damage and ensures the system operates efficiently.
No Heat After Refilling
If the heating system fails to generate heat after refilling, the problem could stem from airlocks, incorrect pressure levels, or a malfunction in the boiler itself. Begin by checking the pressure gauge to confirm that it is within the recommended range. If the pressure is correct, you may need to bleed the radiators to release trapped air that could block the flow of hot water.

Refer to your boiler’s manual for guidance on resolving specific faults that may arise. If these steps do not restore heating, it is advisable to consult a qualified technician to diagnose and fix the underlying issue.
Additional Tips for Maintaining Your Boiler
- Schedule Regular Servicing: Just like any other appliance, regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your boiler in good working condition. It is recommended to have your boiler serviced at least once a year by a qualified technician. This will not only ensure that it is functioning correctly, but also catch any potential issues before they become significant problems.
- Keep an Eye on the Pressure: As mentioned earlier, checking the pressure gauge on your boiler is important for ensuring proper operation. However, it’s also essential to keep an eye on it regularly and make adjustments as needed. If you notice a sudden drop or increase in pressure, this could be a sign of a problem that needs to be addressed. Low pressure can indicate a leak in the system, while high pressure can put unnecessary strain on your boiler and potentially cause damage.
- Bleed Your Radiators: If you have a hot water heating system, it’s essential to bleed your radiators regularly. This involves releasing any trapped air from the system, which can cause cold spots and reduce efficiency.To do this, simply use a radiator key (or a flathead screwdriver) to open the valve at the top of each radiator until you hear hissing or see water come out. Once all the air is released, close the valve and recheck your pressure gauge.
Conclusion
Refilling a boiler after draining is a straightforward process when approached carefully. Start by checking the pressure gauge to ensure it is within the optimal range. Then, locate the filling loop and use it to gradually add water, monitoring the pressure closely to avoid overfilling. Maintaining the correct pressure is essential for the efficient and safe performance of your boiler.
Understanding how to refill boiler after draining helps prevent operational issues and prolongs the system’s lifespan. If you experience persistent problems or feel unsure about the procedure, it’s always best to contact a professional plumber or heating engineer for assistance.

